Sustainable 3D Printing for the Aerospace Industry
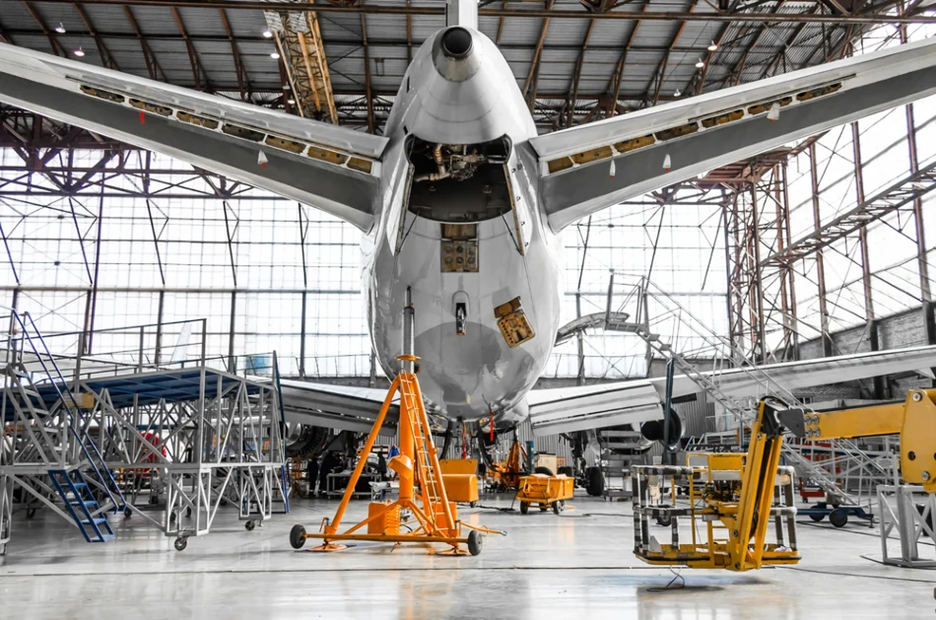

The aerospace industry is a key player in the global push towards sustainability. From reducing the carbon footprint of aircraft to innovating more efficient production methods, aerospace companies are increasingly looking for ways to integrate eco-friendly practices. One such breakthrough technology is 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing. By offering precise, on-demand production capabilities, 3D printing has the potential to drastically reduce material waste and increase fuel efficiency in aircraft production. Let’s explore the role of sustainable 3D printing in the aerospace sector.
1. Reducing Material Waste in Aerospace Manufacturing
Traditional methods of manufacturing in the aerospace industry often result in significant material waste. Techniques such as milling and casting require cutting away large portions of the raw material to shape components, leaving behind substantial scrap. However, 3D printing operates on a layer-by-layer basis, meaning that only the necessary material is used to create a part, minimizing waste.

For example, Boeing and Airbus, two major players in the aerospace industry, have already adopted 3D printing to produce various aircraft components, from brackets to engine parts. By using additive manufacturing, these companies can create parts with minimal waste and only use the material required for the design, which leads to significant reductions in material costs and environmental impact.
2. Lightweight Parts for Improved Fuel Efficiency
Weight reduction is a key factor in increasing fuel efficiency in aircraft. The lighter an aircraft is, the less fuel it requires to operate, reducing emissions and operational costs. 3D printing offers the ability to create intricate, lightweight parts that would be difficult or impossible to produce using traditional manufacturing methods.

By utilizing advanced materials such as titanium and carbon fiber composites, 3D printing can produce high-strength, lightweight components that are ideal for aerospace applications. For instance, GE Aviation has used 3D printing to create lighter turbine blades and fuel nozzles, reducing the overall weight of jet engines and improving their fuel efficiency.
Furthermore, 3D printing allows for the design of parts that are optimized for strength-to-weight ratios, meaning that manufacturers can produce components that are both lighter and stronger than traditionally manufactured ones. This approach contributes to reducing fuel consumption during flights, ultimately lowering the aircraft's carbon emissions.
3. Faster Prototyping and Production
The aerospace industry often deals with long lead times due to the complexity of manufacturing processes. Traditional methods of production require molds and tooling, which can take months to design and produce. With 3D printing, companies can significantly reduce the time required to prototype and manufacture parts.

For example, companies like Airbus have used 3D printing to create parts for the A350 XWB aircraft, allowing them to quickly iterate designs and test them before committing to mass production. This speed not only reduces the environmental impact of waiting for traditional manufacturing methods but also allows for quicker implementation of sustainable materials and designs.
Additionally, 3D printing enables on-demand manufacturing. Components can be produced as needed, reducing the need for excess inventory and unnecessary shipping, which can further reduce the environmental footprint of the production process.
4. Use of Eco-Friendly Materials
One of the major benefits of 3D printing is the variety of materials that can be used, including eco-friendly options. Aerospace manufacturers are increasingly exploring the use of bio-based and recyclable materials for 3D printing parts. For example, researchers are developing bio-plastics and recycled composites that can be used in 3D printing, reducing the need for petroleum-based materials.

Additionally, metal 3D printing allows for the reuse of scrap metal, further contributing to sustainability in the aerospace industry. Materials like titanium and aluminum are commonly used in aerospace components and can be recycled multiple times without losing their strength and integrity. This closed-loop recycling process helps reduce the need for new raw materials, conserving resources and reducing waste.
5. The Future of Sustainable 3D Printing in Aerospace
As the aerospace industry continues to innovate and strive for sustainability, the role of 3D printing will only grow. In the future, we can expect to see even more advanced materials being used in additive manufacturing, including sustainable polymers and composites that will further reduce environmental impact.

Moreover, 3D printing could enable entirely new design possibilities, including more efficient aerodynamics and integrated structures that reduce the need for separate components. This would not only save on material usage but also improve the overall efficiency of the aircraft, leading to further reductions in fuel consumption and emissions.

The integration of 3D printing in aerospace manufacturing is still in its early stages, but the potential benefits are already clear. By reducing material waste, enabling lighter parts, and facilitating faster production cycles, 3D printing is helping the aerospace industry become more sustainable, efficient, and environmentally friendly.
Conclusion
The aerospace industry is poised to benefit significantly from the sustainable practices enabled by 3D printing technology. From reducing material waste to increasing fuel efficiency, 3D printing is making it possible to manufacture lighter, stronger, and more eco-friendly aircraft components. With continued innovation in materials and processes, 3D printing is sure to play a major role in shaping the future of sustainable aerospace manufacturing.
As the demand for greener aviation solutions grows, the adoption of 3D printing in the aerospace industry will continue to be a key factor in reducing the environmental impact of air travel. The future of aviation is green, and 3D printing is helping to get us there.