What is 3D Printing? A Beginner's Guide to Additive Manufacturing
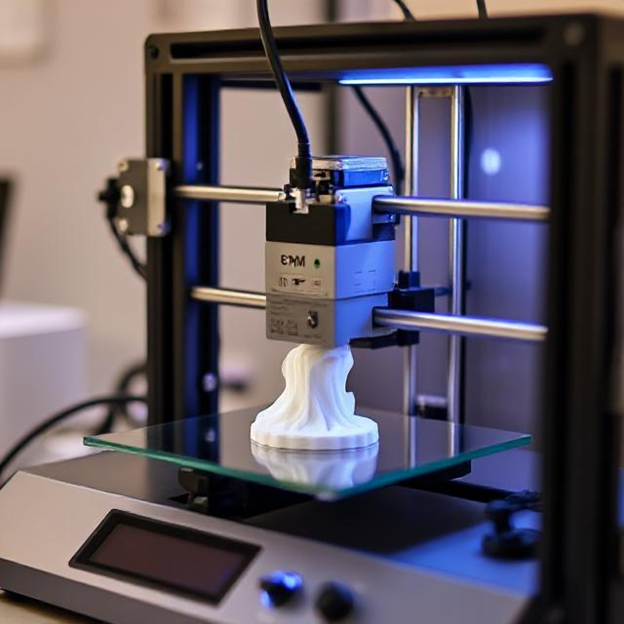

In recent years, 3D printing has emerged as a groundbreaking technology, revolutionizing industries ranging from healthcare and aerospace to fashion and home décor. But what exactly is 3D printing, and why is it gaining so much attention? Let’s dive into the fascinating world of additive manufacturing and explore its significance.
Understanding 3D Printing

3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process of creating three-dimensional objects from a digital file. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods, which often involve cutting, drilling, or molding materials, 3D printing builds objects layer by layer using materials like plastic, resin, metal, and even bio-materials.
How Does 3D Printing Work?
The process of 3D printing follows these key steps:

- Designing the Model – A 3D model is created using specialized software such as Tinkercad, Fusion 360, or Blender. These models are then converted into STL files, which serve as the blueprint for printing.

- Slicing the Model – The digital file is sliced into numerous thin layers using slicing software. This tells the printer how to construct the object layer by layer.

- Printing Process – The 3D printer follows the instructions from the file and starts building the object one layer at a time using the chosen material.
- Post-Processing – Once the object is printed, it may require cleaning, polishing, or additional finishing touches depending on the material and application.
Types of 3D Printing Technologies
There are several types of 3D printing technologies, each catering to different needs:

-
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) – The most common and affordable method, where melted plastic is extruded through a nozzle to form layers.

-
Stereolithography (SLA) – Uses a laser to cure liquid resin into solid objects, known for high precision and smooth finishes.

-
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) – Uses a laser to fuse powdered materials, ideal for strong and durable industrial parts.

-
Metal 3D Printing – Advanced techniques like Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) create metal parts for aerospace and medical applications.
Applications of 3D Printing
3D printing is transforming numerous industries:

-
Healthcare – Prosthetics, dental implants, and even bio-printing human tissues.

-
Automotive & Aerospace – Lightweight, customized parts for vehicles and aircraft.

-
Fashion & Jewelry – Intricate and customizable designs that were previously impossible to produce.

-
Home & DIY Projects – Custom phone cases, tools, and household items made at home.

-
Education – Enhancing learning with physical models for students in engineering, medicine, and design.
Why is 3D Printing Important?

The impact of 3D printing is vast due to its unique advantages: ✅ Customization – Products can be tailored to individual needs. ✅ Waste Reduction – Uses only the necessary material, making it eco-friendly. ✅ Cost Efficiency – Reduces manufacturing costs and material waste. ✅ Rapid Prototyping – Speeds up the development process for new products.
The Future of 3D Printing

With ongoing advancements, 3D printing is expected to revolutionize production across industries. From building houses with concrete 3D printing to bio-printing human organs, the possibilities are endless. As technology evolves, accessibility and affordability will continue to grow, making 3D printing an integral part of our future.
Final Thoughts
3D printing is not just a technological trend; it’s a game-changer that is shaping the way we design, manufacture, and innovate. Whether you're a hobbyist, entrepreneur, or industry professional, embracing 3D printing can open up a world of opportunities.
🚀 Looking for high-quality 3D printed products? Visit: preneel3duniverse.com